Abstract
JAK2 fusions reported in hematologic malignancies are often associated with eosinophilia. In addition to JAK2 fusions such as PCM1-JAK2, BCR-JAK2 and ETV6-JAK2, the JAK2V617Fpoint mutant has been recurrently observed in patients with hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES), occurring in ~4% of patients with hypereosinophilia of unknown significance (Schwaab, Am J Hematol, 2015).
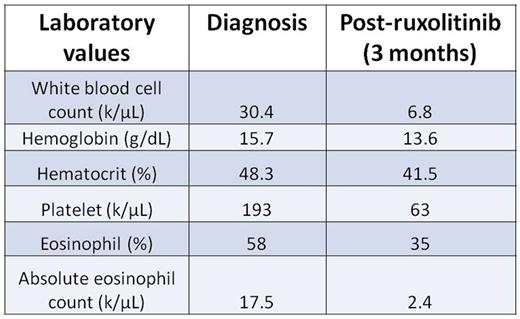
Here, we describe a novel JAK2 mutation in a 69 year-old woman with a history of immune thrombocytopenia referred for steroid-refractory HES. Peripheral blood eosinophilia was present for at least five years, with absolute eosinophil counts ranging up to 17,500/μL. Bone marrow biopsy revealed hypercellular marrow with trilineage hematopoiesis, increased atypical megakaryocytes, and markedly increased eosinophils with abnormal morphology, consistent with myeloproliferative neoplasm. Results from an eosinophilia FISH panel for FIP1L1/CHIC2/PDGFRα, FGFR, PDGFRβ, and CBFβ fusions were negative, as were T-cell clonality studies by next-generation sequencing (NGS). An NGS-based myeloid malignancies panel revealed a novel mutation in JAK2 consisting of a ten base deletion and insertion of a single thymine (JAK2 c.1747_1756delinsT, p.Leu583_Ala586delinsSer;JAK2indel). Treatment with ruxolitinib improved the peripheral blood eosinophilia, but dose intensity was limited by thrombocytopenia (Table 1).
For transformation of cells to cytokine-independence, JAK2V617F requires co-expression of a type I dimeric cytokine receptor, such as Epo-R, to enable downstream signaling in the absence of growth factors (Lu et al, Proc Natl Acad Sci, 2005). To characterize the signaling properties of the new JAK2indel mutant, we cloned JAK2WT, JAK2V617F, and JAK2indel into the MSCV-IRES-GFP (MIG) retroviral vector. IL-3-dependent Ba/F3 cells lacking type I cytokine receptors were infected with retrovirus to assess cytokine independence.
Parental Ba/F3 cells and those transduced with JAK2WT, JAK2V617F, or JAK2indel proliferated at similar rates when grown in WEHI conditioned medium (CM). However, upon IL-3 (WEHI) withdrawal, only GFP-positive JAK2indel Ba/F3 cells demonstrated growth factor independence (n=3). Furthermore, parental and GFP-sorted JAK2WT- and JAK2V617F-expressingBa/F3 cells display acceleration of growth when cultured in graded dilutions of WEHI CM, while growth of JAK2indel Ba/F3 cells is not further enhanced by WEHI CM. JAK2indel-expressing Ba/F3 cells also demonstrated cytokine-independent growth in colony assays, whereas parental, JAK2WT-, and JAK2V617F-expressing cells displayed little to no colony formation in the absence of cytokines. Immunoblot analyses revealed that after 4 hours of culture ± IL-3, all cells grown in IL-3 demonstrated activation of STAT5 and ERK, but only JAK2indel Ba/F3 cells demonstrated cytokine-independent signaling activation.
JAK2indel activates STAT5 and ERK without co-expression of a type I cytokine receptor, implicating a mechanism of JAK2 kinase activation that is distinct from JAK2V617F. Unexpectedly, preliminary structural analysis suggests that the conformational change induced by JAK2indel resembles that of JAK2V617F. Mutation of glutamic acid 596 to arginine (E596R) has been shown to abolish the constitutive activity of JAK2V617F via modulation of the C-terminal residues of the SH2-JH2 linker, thereby restoring pseudokinase domain autoinhibitory function (Leroy et al, Biochem J, 2016). To test whether this regulatory mechanism is preserved in JAK2indel, we introduced E596R into JAK2indel and are currently characterizing JAK2indel/E596R in cellular and biochemical assays. Additional modeling and biochemical work is underway to clarify whether JAK2indel confers a new functionality that supports signaling activation in the absence of a type I cytokine receptor.
In summary we report a novel JAK2 mutation in a patient with myeloproliferative-variant HES that results in cytokine-independent growth, is associated with STAT5 and ERK phosphorylation and may be employing an alternative mechanism to achieve constitutive activation of signaling. The fact that the patient's eosinophilia improved with ruxolitinib treatment illustrates the importance of performing NGS in patients with HES to identify potentially targetable genetic lesions.
Deininger: Ariad Pharmaceuticals, Bristol Myers Squibb, CTI BioPharma Corp, Gilead, Incyte, Novartis, Pfizer, Celgene, Blue Print, Galena: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead: Research Funding; Incyte: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; ARIAD: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.